Key to the Heart: Heart Rate Variability
What is Heart Rate Variability (HRV)?
Heart rate variability (HRV) measures the variance between each heartbeat. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) controls this variance. The ANS works in the background, regulating essential functions such as heart rate, blood pressure, breathing, and digestion.
It consists of two branches. The sympathetic nervous system prepares your body for action with a “fight or flight” response. In contrast, the parasympathetic nervous system supports rest and recovery.
How the Brain Affects HRV
Your brain sends signals to the ANS through the hypothalamus. These signals either activate or relax specific body functions depending on your needs. This system helps you adjust to different situations—from stress at work to calm during sleep—without disrupting your internal balance.
Why HRV Matters
HRV is a key indicator of how well your two ANS branches stay in balance. A high HRV shows a flexible, adaptive nervous system. This flexibility allows your body to manage physical or emotional stress and recover quickly. On the other hand, a low HRV often reflects chronic stress, poor sleep, or possible health issues.
How to Calculate HRV
To measure HRV accurately, you need equipment that tracks tiny differences between heartbeats, measured in milliseconds. Most calculations rely on two formulas:
The root mean square of successive differences (RMSSD) between normal heartbeats
The standard deviation of normal intervals (SDNN)
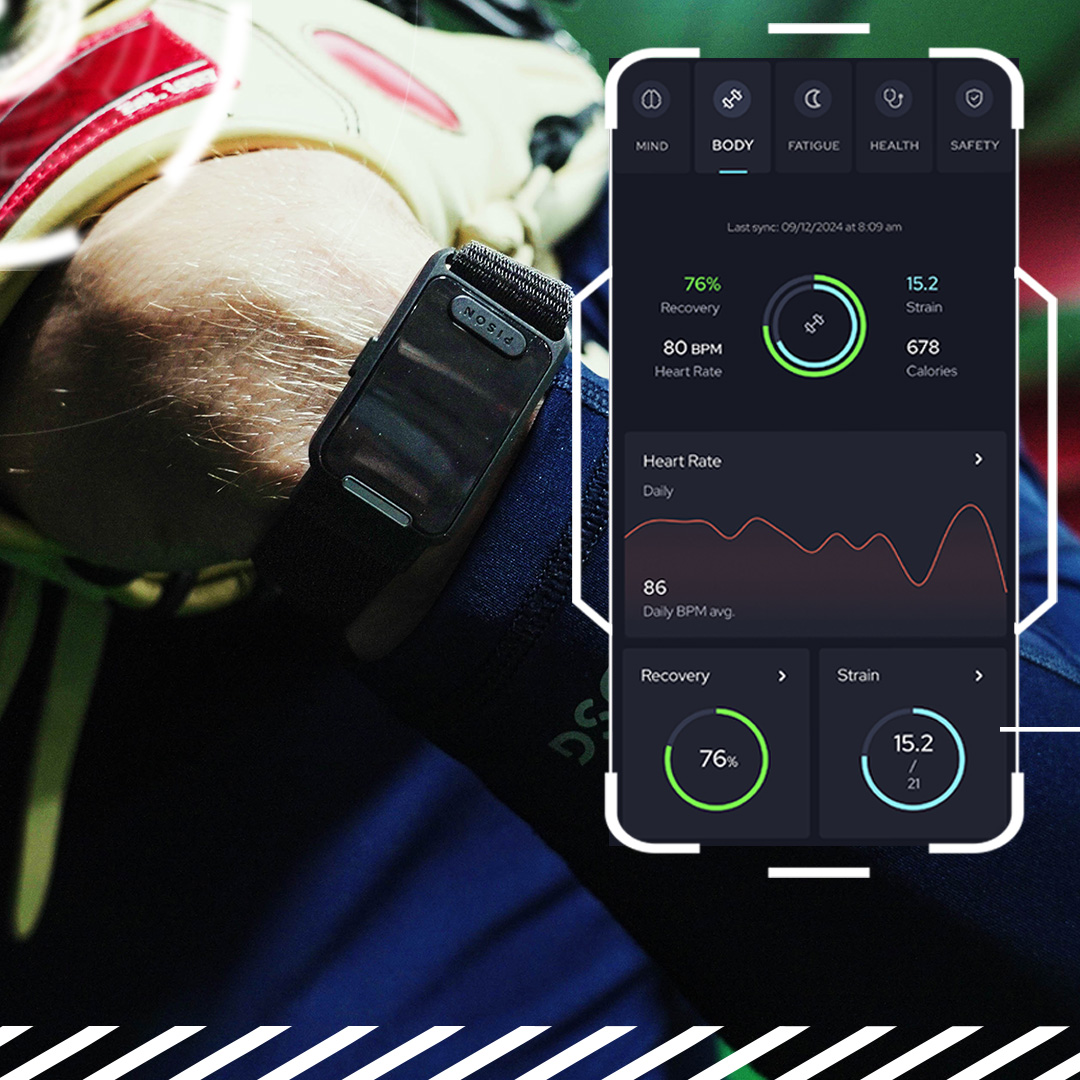
Doctors often use electrocardiograms (EKGs) for this purpose. These are the traditional gold standard. However, newer wearable devices—such as chest straps or smart trackers like Pison Perform—also offer reliable HRV readings for everyday use.
For best results, measure HRV in the morning while your body is still at rest. Longer data collection, such as over 24 hours, provides a more complete picture of your heart’s behavior.
Interpreting HRV Data
HRV levels vary based on age and gender. Young adults usually have higher HRV, while older adults tend to show a gradual decline. Hormonal differences may also affect HRV patterns between men and women. These factors are important when interpreting your results.
| Age Group | Average HRV (ms) |
|---|---|
| 18–25 | 62–85 |
| 26–35 | 55–75 |
| 36–45 | 50–70 |
| 46–55 | 45–65 |
| 56–65 | 42–62 |
| 66+ | 40–60 |
An HRV between 60 and 100 ms typically signals good health. Readings over 100 are often associated with excellent health, while values under 60 may indicate elevated stress or health concerns.
Improving HRV
You can raise your HRV by focusing on both physical and mental wellness. Below are effective strategies:
Regular Exercise
Aerobic activities—such as running, cycling, or swimming—strengthen the heart and improve HRV. Consistency matters more than intensity.
Healthy Diet
A nutrient-rich, balanced diet supports cardiovascular function and overall health.
Stress Management
Techniques like mindfulness, meditation, or deep breathing can boost HRV. One effective method is box breathing, also known as diaphragmatic breathing, which helps calm the nervous system.
Quality Sleep
Aim for 7 to 9 hours of uninterrupted sleep each night. Your body needs this rest to maintain a strong and balanced HRV.
Biofeedback Training
This technique uses technology to help you track and influence bodily responses. Over time, biofeedback can reduce stress and improve HRV.
Health Implications of HRV
HRV serves as a powerful, non-invasive marker of autonomic nervous system health. While athletes use it to fine-tune performance, HRV also holds value for medical professionals. It helps detect or monitor issues such as anxiety, depression, heart disease, and sleep disorders.
Research shows that HRV can predict cardiovascular risks and reveal how well someone copes with stress. Athletes, in particular, use HRV data to manage training intensity, recovery, and prevent overtraining. This approach helps optimize performance while protecting long-term health.